# 使用网络方法识别疾病模块
在 2015 年的一篇 Science "Uncovering disease-disease relationships through the incomplete interactome" 中,作者提出了一种基于网络距离的方法来识别和分析疾病模块,并揭示疾病之间的关系。
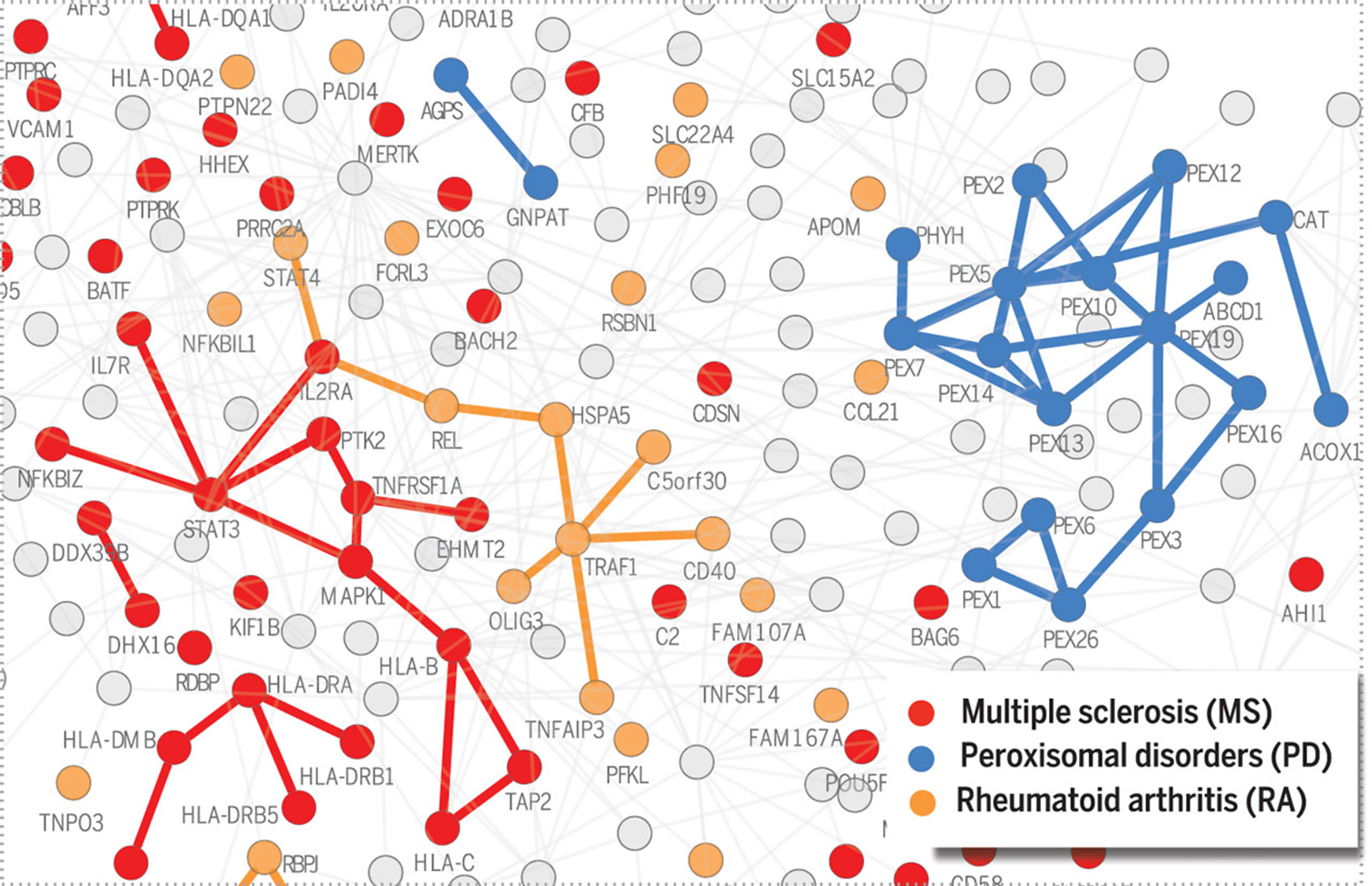
# 背景
疾病不是由单个基因异常直接导致的,而是由多个分子过程的相互作用所引起的。这些过程之间的关系被编码在相互作用网络(interactome)中,这个网络集成了细胞内所有的物理相互作用,包括蛋白质 - 蛋白质、调控蛋白质 - DNA 和代谢相互作用。
研究表明,疾病相关的蛋白质往往聚集在相互作用网络的同一邻域内,形成一个疾病模块。
研究显示只有当与疾病相关的基因数量超过某个临界值时,我们才能揭示疾病模块。研究发现,与 226 种疾病相关的蛋白质在同一网络邻域内聚集,表现出显著的形成可识别疾病模块的趋势。疾病蛋白质在网络中的聚集程度越高,相应基因的生物学和功能相似性越高。
# 方法
文章的补充文件中提供了两个 Python 脚本:
# separation.py
这个脚本用于计算基于网络的距离 和分离度 ,用以表示两个给定基因集 和 在给定网络上的相对位置和分离度。
# localization.py
此脚本的主要功能是计算一个给定基因集在相互作用网络中的本地化特性。它会计算以下 3 个指标:
- 最大连通子图的大小 (S):给定基因集在相互作用网络中形成的最大连通子图(LCC)的大小。
- 平均最短路径长度 (d_s):基因集内所有基因对之间的平均最短路径长度。
- 随机期望值:通过随机模拟生成相同数量的基因集,并计算这些随机基因集的最大连通子图大小的期望值和标准差,然后比较实际基因集的结果,输出 z-score。
然而,给出的代码都是基于 Python2 语法的,现在主流的 Python 版本是 Python3,所以我用 Python3 的语法重写了这两个脚本。
# 重写后的代码
# separation_py3.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3 | |
""" | |
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
# | |
# separation_py3.py | |
# | |
# by Joerg Menche | |
# Last Modified: 2014-12-06 | |
# | |
# This code determines the network-based distance and separation for | |
# two given sets of nodes on a given network as described in | |
# | |
# Uncovering Disease-Disease Relationships Through The Human | |
# Interactome | |
# | |
# by Joerg Menche, Amitabh Sharma, Maksim Kitsak, Susan Dina | |
# Ghiassian, Marc Vidal, Joseph Loscalzo & Albert-Laszlo Barabasi | |
# | |
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
# | |
# This program will calculate the network-based distance d_AB and | |
# separation s_AB between two gene sets A and B. | |
# | |
# * Required input: | |
# | |
# two files containing the gene sets A and B. The file must be in | |
# form of a table, one gene per line. If the table contains several | |
# columns, they must be tab-separated, only the first column will be | |
# used. See the two files MS.txt and PD.txt for valid examples (they | |
# contain genes for multiple sclerosis and peroxisomal disorders, | |
# respectively). | |
# | |
# * Optional input: | |
# | |
# - file containing an interaction network. If no file is given, the | |
# default network "interactome.tsv" will be used instead. The file | |
# must contain an edgelist provided as a tab-separated table. The | |
# first two columns of the table will be interpreted as an | |
# interaction gene1 <==> gene2 | |
# | |
# - filename for the output. If none is given, | |
# "separation_results.txt" will be used | |
# | |
# | |
# Here's an example that should work, provided the files are in the same | |
# directory as this python script: | |
# | |
# ./separation_py3.py -n interactome.tsv --g1 MS.txt --g2 PD.txt -o output.txt | |
# | |
# | |
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
""" | |
import networkx as nx | |
import numpy as np | |
import argparse | |
import sys | |
""" | |
# ============================================================================= | |
S T A R T D E F I N I T I O N S | |
# ============================================================================= | |
""" | |
def print_usage(): | |
""" | |
打印使用说明 | |
""" | |
usage_message = """ | |
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
This program will calculate the network-based distance d_AB and | |
separation s_AB between two gene sets A and B. | |
* Required input: | |
two files containing the gene sets A and B. The file must be in form | |
of a table, one gene per line. If the table contains several | |
columns, they must be tab-separated, only the first column will be | |
used. See the two files MS.txt and PD.txt for valid examples (they | |
contain genes for multiple sclerosis and peroxisomal disorders, | |
respectively). | |
* Optional input: | |
- file containing an interaction network. If no file is given, the | |
default network \"interactome.tsv\" will be used instead. The file | |
must contain an edgelist provided as a tab-separated table. The | |
first two columns of the table will be interpreted as an | |
interaction gene1 <==> gene2 | |
- filename for the output. If none is given, | |
\"separation_results.txt\" will be used | |
Here's an example that should work, provided the files are in the same | |
directory as this python script: | |
./separation_py3.py -n interactome.tsv --g1 MS.txt --g2 PD.txt -o output.txt | |
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
""" | |
print(usage_message) | |
sys.exit() | |
def read_network(network_file): | |
""" | |
读取网络文件并构建图 | |
* 边列表必须是制表符分隔的表。表的前两列将被解释为 | |
相互作用 gene1 <==> gene2 | |
* 以 '#' 开头的行将被忽略 | |
""" | |
G = nx.Graph() | |
with open(network_file, 'r') as file: | |
for line in file: | |
# 忽略以 '#' 开头的行 | |
if line.startswith('#'): | |
continue | |
# 解析行中的前两列作为交互节点 | |
node1, node2 = line.strip().split('\t')[:2] | |
G.add_edge(node1, node2) | |
print("\n> done loading network:") | |
print("> network contains {} nodes and {} links".format(G.number_of_nodes(), G.number_of_edges())) | |
return G | |
def read_gene_list(gene_file): | |
""" | |
从外部文件读取基因列表。 | |
* 基因必须作为表提供。如果表有多列,则它们必须是 | |
制表符分隔。只使用第一列。 | |
* 以 '#' 开头的行将被忽略 | |
""" | |
genes_set = set() | |
with open(gene_file, 'r') as file: | |
for line in file: | |
if line.startswith('#'): | |
continue | |
gene = line.strip().split('\t')[0] | |
genes_set.add(gene) | |
print("\n> done reading genes:") | |
print("> {} genes found in {}".format(len(genes_set), gene_file)) | |
return genes_set | |
def remove_self_links(G): | |
""" | |
移除图中的自环边 | |
""" | |
sl = list(nx.selfloop_edges(G)) | |
G.remove_edges_from(sl) | |
def get_pathlengths_for_single_set(G, given_gene_set): | |
""" | |
计算给定基因集合中各基因对之间的最短路径长度。 | |
结果存储在字典中: | |
all_path_lengths[gene1][gene2] = l | |
其中 gene1 < gene2,因此每对只存储一次 | |
参数: | |
- G: 网络 | |
- gene_set: 要计算路径的基因集 | |
返回: | |
- all_path_lengths[gene1][gene2] = l | |
""" | |
# 去除不在网络中的节点 | |
all_genes_in_network = set(G.nodes()) | |
gene_set = given_gene_set & all_genes_in_network | |
all_path_lengths = {} | |
# 计算所有可能对的距离 | |
for gene1 in gene_set: | |
if gene1 not in all_path_lengths: | |
all_path_lengths[gene1] = {} | |
for gene2 in gene_set: | |
if gene1 < gene2: | |
try: | |
l = nx.shortest_path_length(G, source=gene1, target=gene2) | |
all_path_lengths[gene1][gene2] = l | |
except nx.NetworkXNoPath: | |
continue | |
return all_path_lengths | |
def get_pathlengths_for_two_sets(G, given_gene_set1, given_gene_set2): | |
""" | |
计算两个给定基因集合中各基因对之间的最短路径长度。 | |
结果存储在字典中:all_path_lengths[gene1][gene2] = l | |
其中 gene1 < gene2,因此每对只存储一次 | |
参数: | |
- G: 网络 | |
- gene_set1/2: 要计算路径的基因集 | |
返回: | |
- all_path_lengths[gene1][gene2] = l | |
""" | |
# 去除不在网络中的节点 | |
all_genes_in_network = set(G.nodes()) | |
gene_set1 = given_gene_set1 & all_genes_in_network | |
gene_set2 = given_gene_set2 & all_genes_in_network | |
all_path_lengths = {} | |
# 计算所有可能对的距离 | |
for gene1 in gene_set1: | |
if gene1 not in all_path_lengths: | |
all_path_lengths[gene1] = {} | |
for gene2 in gene_set2: | |
if gene1 != gene2: | |
try: | |
l = nx.shortest_path_length(G, source=gene1, target=gene2) | |
if gene1 < gene2: | |
all_path_lengths[gene1][gene2] = l | |
else: | |
if gene2 not in all_path_lengths: | |
all_path_lengths[gene2] = {} | |
all_path_lengths[gene2][gene1] = l | |
except nx.NetworkXNoPath: | |
continue | |
return all_path_lengths | |
def calc_single_set_distance(G, given_gene_set): | |
""" | |
计算给定网络中基因集合的平均最短距离 | |
参数: | |
- G: 网络 | |
- gene_set: 要计算距离的基因集 | |
返回: | |
- 平均最短距离 | |
""" | |
# 去除不在网络中的节点 | |
all_genes_in_network = set(G.nodes()) | |
gene_set = given_gene_set & all_genes_in_network | |
# 获取所有基因对的网络距离 | |
all_path_lengths = get_pathlengths_for_single_set(G, gene_set) | |
all_distances = [] | |
# 遍历所有基因对 | |
for geneA in gene_set: | |
all_distances_A = [] | |
for geneB in gene_set: | |
if geneA < geneB: | |
if geneB in all_path_lengths[geneA]: | |
all_distances_A.append(all_path_lengths[geneA][geneB]) | |
else: | |
if geneA in all_path_lengths[geneB]: | |
all_distances_A.append(all_path_lengths[geneB][geneA]) | |
if all_distances_A: | |
l_min = min(all_distances_A) | |
all_distances.append(l_min) | |
# 计算平均最短距离 | |
mean_shortest_distance = np.mean(all_distances) | |
return mean_shortest_distance | |
def calc_set_pair_distances(G, given_gene_set1, given_gene_set2): | |
""" | |
计算给定网络中两个基因集合之间的平均最短距离 | |
参数: | |
- G: 网络 | |
- gene_set1/2: 要计算距离的基因集 | |
返回: | |
- 平均最短距离 | |
""" | |
# 去除不在网络中的节点 | |
all_genes_in_network = set(G.nodes()) | |
gene_set1 = given_gene_set1 & all_genes_in_network | |
gene_set2 = given_gene_set2 & all_genes_in_network | |
# 获取所有基因对的网络距离 | |
all_path_lengths = get_pathlengths_for_two_sets(G, gene_set1, gene_set2) | |
all_distances = [] | |
# 遍历所有基因对,从集合 1 开始 | |
for geneA in gene_set1: | |
all_distances_A = [] | |
for geneB in gene_set2: | |
if geneA == geneB: | |
all_distances_A.append(0) | |
else: | |
if geneA < geneB: | |
try: | |
all_distances_A.append(all_path_lengths[geneA][geneB]) | |
except KeyError: | |
pass | |
else: | |
try: | |
all_distances_A.append(all_path_lengths[geneB][geneA]) | |
except KeyError: | |
pass | |
if all_distances_A: | |
l_min = min(all_distances_A) | |
all_distances.append(l_min) | |
# 遍历所有基因对,从集合 2 开始 | |
for geneA in gene_set2: | |
all_distances_A = [] | |
for geneB in gene_set1: | |
if geneA == geneB: | |
all_distances_A.append(0) | |
else: | |
if geneA < geneB: | |
try: | |
all_distances_A.append(all_path_lengths[geneA][geneB]) | |
except KeyError: | |
pass | |
else: | |
try: | |
all_distances_A.append(all_path_lengths[geneB][geneA]) | |
except KeyError: | |
pass | |
if all_distances_A: | |
l_min = min(all_distances_A) | |
all_distances.append(l_min) | |
# 计算平均最短距离 | |
mean_shortest_distance = np.mean(all_distances) | |
return mean_shortest_distance | |
""" | |
# ============================================================================= | |
E N D O F D E F I N I T I O N S | |
# ============================================================================= | |
""" | |
if __name__ == '__main__': | |
# "Hey Ho, Let's go!" -- The Ramones (1976) | |
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() | |
parser.add_argument('-u', '--usage', help='print more info on how to use this script', action='store_true') | |
parser.add_argument('-n', help='file containing the network edgelist [interactome.tsv]', dest='network_file', default='interactome.tsv', type=str) | |
parser.add_argument('--g1', help='file containing gene set 1', dest='gene_file_1', default='none', type=str) | |
parser.add_argument('--g2', help='file containing gene set 2', dest='gene_file_2', default='none', type=str) | |
parser.add_argument('-o', help='file for results [separation_results.txt]', dest='results_file', default='separation_results.txt', type=str) | |
args = parser.parse_args() | |
if args.usage: | |
print_usage() | |
network_file = args.network_file | |
gene_file_1 = args.gene_file_1 | |
gene_file_2 = args.gene_file_2 | |
results_file = args.results_file | |
# 检查输入文件: | |
if gene_file_1 == 'none' or gene_file_2 == 'none': | |
error_message = """ | |
ERROR: you must specify two files with gene sets, for example: | |
./separation_py3.py --g1 MS.txt --g2 PD.txt | |
For more information, type | |
./separation_py3.py --usage | |
""" | |
print(error_message) | |
sys.exit(0) | |
if network_file == 'interactome.tsv': | |
print('> default network from "interactome.tsv" will be used') | |
# 读取网络和疾病基因集 | |
G = read_network(network_file) | |
all_genes_in_network = set(G.nodes()) | |
remove_self_links(G) | |
# 读取基因集 1 | |
genes_A_full = read_gene_list(gene_file_1) | |
genes_A = genes_A_full & all_genes_in_network | |
if len(genes_A_full) != len(genes_A): | |
print("> ignoring {} genes that are not in the network".format(len(genes_A_full - all_genes_in_network))) | |
print("> remaining number of genes: {}".format(len(genes_A))) | |
# 读取基因集 2 | |
genes_B_full = read_gene_list(gene_file_2) | |
genes_B = genes_B_full & all_genes_in_network | |
if len(genes_B_full) != len(genes_B): | |
print("> ignoring {} genes that are not in the network".format(len(genes_B_full - all_genes_in_network))) | |
print("> remaining number of genes: {}".format(len(genes_B))) | |
# 计算网络量化指标 | |
d_A = calc_single_set_distance(G, genes_A) | |
d_B = calc_single_set_distance(G, genes_B) | |
d_AB = calc_set_pair_distances(G, genes_A, genes_B) | |
s_AB = d_AB - (d_A + d_B) / 2.0 | |
results_message = """ | |
> gene set A from "{}": {} genes, network-diameter d_A = {} | |
> gene set B from "{}": {} genes, network-diameter d_B = {} | |
> mean shortest distance between A & B: d_AB = {} | |
> network separation of A & B: s_AB = {} | |
""".format(gene_file_1, len(genes_A), d_A, gene_file_2, len(genes_B), d_B, d_AB, s_AB) | |
print(results_message) | |
with open(results_file, 'w') as fp: | |
fp.write(results_message) | |
print("> results have been saved to {}".format(results_file)) |
# localization_py3.py
#! /usr/bin/env python3 | |
""" | |
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
# | |
# localization_py3.py | |
# | |
# by Joerg Menche | |
# Last Modified: 2014-12-06 | |
# | |
# This code determines the network-based distance and separation for | |
# two given sets of nodes on a given network as described in | |
# | |
# Uncovering Disease-Disease Relationships Through The Human | |
# Interactome | |
# | |
# by Joerg Menche, Amitabh Sharma, Maksim Kitsak, Susan Dina | |
# Ghiassian, Marc Vidal, Joseph Loscalzo & Albert-Laszlo Barabasi | |
# | |
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
# | |
# This program will calculate the size of the largest connected | |
# component S and mean shortest distance <d_s> for a given gene | |
# set. It will also compute the expected lcc size for the same number | |
# of randomly distributed genes. | |
# | |
# * Required input: | |
# | |
# a file containing a gene set. The file must be in form of a table, | |
# one gene per line. If the table contains several columns, they | |
# must be tab-separated, only the first column will be used. See the | |
# two files MS.txt and PD.txt for valid examples (they contain genes | |
# for multiple sclerosis and peroxisomal disorders, respectively). | |
# | |
# * Optional input: | |
# | |
# - file containing an interaction network. If no file is given, the | |
# default network "interactome.tsv" will be used instead. The file | |
# must contain an edgelist provided as a tab-separated table. The | |
# first two columns of the table will be interpreted as an | |
# interaction gene1 <==> gene2 | |
# | |
# - filename for the output. If none is given, | |
# "localization_results.txt" will be used | |
# | |
# - the number or random simulations can be chosen. Default is 1000, | |
# which should run fast even for large gene sets and typically | |
# gives good results. | |
# | |
# Here's an example that should work, provided the files are in the same | |
# directory as this python script: | |
# | |
# ./localization_py3.py -n interactome.tsv -g PD.txt -o output.txt | |
# | |
# | |
# ----------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
""" | |
import networkx as nx | |
import random | |
import numpy as np | |
import argparse | |
import sys | |
import separation_py3 as tools | |
""" | |
# ============================================================================= | |
S T A R T D E F I N I T I O N S | |
# ============================================================================= | |
""" | |
def print_usage(): | |
""" | |
打印使用说明 | |
""" | |
usage_message = """ | |
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
This program will calculate the network-based localization for a given | |
gene set | |
* Required input: | |
one file containing a gene set. The file must be in form of a | |
table, one gene per line. If the table contains several columns, | |
they must be tab-separated, only the first column will be used. See | |
the two files MS.txt and PD.txt for valid examples (they contain | |
genes for multiple sclerosis and peroxisomal disorders). | |
* Optional input: | |
- file containing an interaction network. If no file is given, the | |
default network \"interactome.tsv\" will be used instead. The file | |
must contain an edgelist provided as a tab-separated table. The | |
first two columns of the table will be interpreted as an | |
interaction gene1 <==> gene2 | |
- filename for the output. If none is given, | |
\"localization_results.txt\" will be used | |
- the number or random simulations can be chosen. Default is 1000, | |
which should run fast even for large gene sets and typically gives | |
good results. | |
Here's an example that should work, provided the files are in the same | |
directory as this python script: | |
./localization_py3.py -n interactome.tsv -g PD.txt -o output.txt | |
# ---------------------------------------------------------------------- | |
""" | |
print(usage_message) | |
sys.exit() | |
def get_lcc_size(G, seed_nodes): | |
""" | |
返回最大连通组件的大小 | |
""" | |
g = G.subgraph(seed_nodes) | |
if g.number_of_nodes() != 0: | |
components = nx.connected_components(g) | |
return len(next(components)) | |
else: | |
return 0 | |
def get_random_comparison(G, gene_set, sims): | |
""" | |
获取随机基因集的最大连通组件大小期望值 | |
参数: | |
- G: 网络 | |
- gene_set: 基因集 | |
- sims: 随机模拟次数 | |
返回: | |
- 包含结果的字符串 | |
""" | |
all_genes = list(G.nodes()) | |
number_of_seed_genes = len(gene_set & set(all_genes)) | |
l_list = [] | |
print("") | |
for i in range(1, sims + 1): | |
if i % 100 == 0: | |
sys.stdout.write("> random simulation [{} of {}]\r".format(i, sims)) | |
sys.stdout.flush() | |
rand_seeds = set(random.sample(all_genes, number_of_seed_genes)) | |
lcc = get_lcc_size(G, rand_seeds) | |
l_list.append(lcc) | |
lcc_observed = get_lcc_size(G, gene_set) | |
l_mean = np.mean(l_list) | |
l_std = np.std(l_list) | |
if l_std == 0: | |
z_score = 'not available' | |
else: | |
z_score = (lcc_observed - l_mean) / l_std | |
results_message = """ | |
> Random expectation: | |
> lcc [rand] = {} | |
> => z-score of observed lcc = {} | |
""".format(l_mean, z_score) | |
return results_message | |
""" | |
# ============================================================================= | |
E N D O F D E F I N I T I O N S | |
# ============================================================================= | |
""" | |
if __name__ == '__main__': | |
# "Hey Ho, Let's go!" -- The Ramones (1976) | |
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser() | |
parser.add_argument('-u', '--usage', | |
help='print more info on how to use this script', | |
action='store_true') | |
parser.add_argument('-n', | |
help='file containing the network edgelist [interactome.tsv]', | |
dest='network_file', | |
default='interactome.tsv', | |
type=str) | |
parser.add_argument('-g', | |
help='file containing gene set', | |
dest='gene_file', | |
default='none', | |
type=str) | |
parser.add_argument('-s', | |
help='number of random simulations [1000]', | |
dest='sims', | |
default=1000, | |
type=int) | |
parser.add_argument('-o', | |
help='file for results [localization_results.txt]', | |
dest='results_file', | |
default='localization_results.txt', | |
type=str) | |
args = parser.parse_args() | |
if args.usage: | |
print_usage() | |
network_file = args.network_file | |
gene_file = args.gene_file | |
results_file = args.results_file | |
sims = args.sims | |
if gene_file == 'none': | |
print(""" | |
ERROR: you must specify an input file with a gene set, for example: | |
./localization_py3.py -g MS.txt | |
For more information, type | |
./localization_py3.py --usage | |
""") | |
sys.exit(0) | |
if network_file == 'interactome.tsv': | |
print('> default network from "interactome.tsv" will be used') | |
G = tools.read_network(network_file) | |
all_genes_in_network = set(G.nodes()) | |
tools.remove_self_links(G) | |
gene_set_full = tools.read_gene_list(gene_file) | |
gene_set = gene_set_full & all_genes_in_network | |
if len(gene_set_full) != len(gene_set): | |
print("> ignoring {} genes that are not in the network".format( | |
len(gene_set_full - all_genes_in_network))) | |
print("> remaining number of genes: {}".format(len(gene_set))) | |
lcc = get_lcc_size(G, gene_set) | |
print("\n> lcc size = {}".format(lcc)) | |
d_s = tools.calc_single_set_distance(G, gene_set) | |
print("> mean shortest distance = {}".format(d_s)) | |
results_message = """ | |
> gene set from "{}": {} genes | |
> lcc size S = {} | |
> diameter d_s = {} | |
""".format(gene_file, len(gene_set), lcc, d_s) | |
results_message += get_random_comparison(G, gene_set, sims) | |
print(results_message) | |
with open(results_file, 'w') as fp: | |
fp.write(results_message) | |
print("> results have been saved to {}".format(results_file)) |